Urologic problems or diseases are conditions that affect any part of the urinary system and the male genitalia.
The urinary system (or renal system) is called as such since it’s the producer of urine (pee), the body’s natural by-product from the various metabolic processes. It also contains excess water the body doesn’t need.
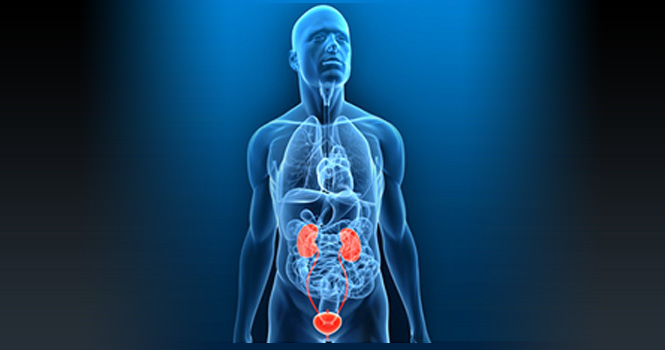
It is composed mainly of the kidneys, ureter, bladder, sphincter muscles, and the urethra, which can differ in length between men and women (women have a shorter urethra than men).
The kidneys are the bean-shaped organs found on each side of the body and near the adrenal glands. Although small, they play a major part in the urinary system since they are the ones responsible for filtering toxins and other wastes from the body. They also help keep the electrolyte balance. The urine, which contains the toxins and excess water, then travels through the ureter, which is connected to the bladder.
The bladder can be likened to a balloon, which expands once urine starts coming in and, therefore, controls the elimination of urine. Once the bladder is full, the nerves found on the bladder walls send the message to the brain, so the body reacts and prepares itself for urination.
The urine then passes through the sphincter muscles, which are now relaxed, and into the urethra. It goes out of the vaginal opening or the penis.
The male reproductive system, on the other hand, is made up of the penis, scrotum, bladder, prostate, urethra, vas deferens, epididymis, and testicle. Unlike those of women, the male reproductive parts are more visible. The penis is where the sperm cells (male reproductive cells) are expelled during sexual intercourse or ejaculation. The scrotum is the small sac that hangs behind the penis. It is responsible for keeping the testes, which produce the sperm and the male sex hormones, in an ideal condition. The sperm produced by the testes travels to the epididymis, which stores and allows it to mature for fertilization and reproduction. Then, it goes through the vas deferens and into the urethra.
Causes of Condition
Here are some of the most common causes of urology problems:
- Infection – Infection such as urinary tract infection (UTI) can happen to males though it’s more common among women. Harmful microorganisms such as bacteria can get into the body through the anus until they invade the urethra, making it painful to urinate. Although UTI is easy to treat, when left unmanaged, it can cause serious complications including septic shock that results in organ failure and death.
- Obstruction – Kidneys, for example, can develop stones that may block the flow of urine to the bladder. Obstructions can also occur in the vas deferens and prostate.
- Lifestyle factors – Obesity is currently one of the biggest threats on chronic kidney disease (CKD) risk. CKD is usually associated with elevated blood pressure and diabetes, which are also related to obesity. A person may suffer from CKD without any symptom. Unfortunately, once it’s discovered, it is usually already in the late or end stage.
- Heredity – Polycystic kidney disease is an inherited disorder characterized by the presence of several fluid-filled sacs in the kidneys. They can multiply and grow large. They can also break causing severe bleeding and pain when urinating. They can damage the kidneys in the long run as they promote high blood pressure.
- Diuretics or medications – Certain medications such as diuretics promote the production of urine, which may lead to excessive urination or incontinence. Some drugs can also be harmful to the kidneys in the long term.
- Food – Alcohol and caffeine may also act as diuretics.
- Congenital – Many abnormalities can affect the male genitalia such as micropenis and chordee (in which the penis’s head is curved either downward or upward).
- Physiological – Male infertility can be caused by poor or low sperm production, ejaculation issues, and hormonal imbalances.
- Unknown causes – Some disorders don’t have a definite cause. A good example is interstitial cystitis, which is also called painful bladder syndrome. Researchers point to an autoimmune disease, heredity, genetic defect, and infection as possible causes.
Key Symptoms
- Difficulty of passing urine
- Abnormal volume of urine (may be too much or too small)
- Lower back (flank) pain
- Pain in the lower abdomen
- Fever
- Passing off blood during urination (hematuria)
- Pain during urination
- Frequent urge to pass urine
- Feeling of not emptying the bladder
- Nausea and vomiting
- Change of urine color and smell
- Enlarged prostate
- Urine leakage
- Loss of bladder control (incontinence)
Who to See and Treatments Available
Renal problems can be diagnosed and treated by a urologist. Since the problems can also occur among children, parents can find one that specializes in pediatrics. Some urologists also master oncology and surgery.
Although both urologists and nephrologists deal with kidney problems, any issue about the male reproductive system is handled by a urologist.
There are many ways to diagnose a potential problem. One of the most effective and easiest methods is urinalysis, which can reveal any presence of blood, crystal deposits, or even stones, as well as bacteria that may be causing infection. Blood tests can reveal issues affecting the hormones. Ultrasound can also be helpful, as well as imaging tests such as CT and MRI, since they can reveal any blockages such as tumors or presence of cancer cells.
Treatments vary depending on the diagnosis. These include:
- Surgery, which can remove blockages or diseased body parts such as kidneys (a person can live with one kidney only as long as it’s healthy), as well as correct abnormalities
- Medications like antibiotics to treat infection, reduce inflammation, or treat the underlying disease that’s causing the urology problem
- Radiation and chemotherapy for urology-related cancers
- Reproductive-assisted methods for males who are having hard time to conceive due to sperm issues
- Counseling for male who suffer from mental health issues that lead to premature ejaculation or erectile dysfunction
Many of the diseases can also be controlled or the risk reduced by lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, eating a diet that’s low in fat and sodium, and exercising regularly.
SOURCE – DocDoc
Thanks for sharing.
ReplyDeleteIf you are searching for a Reputed Urologist in Ludhiana then contact us.